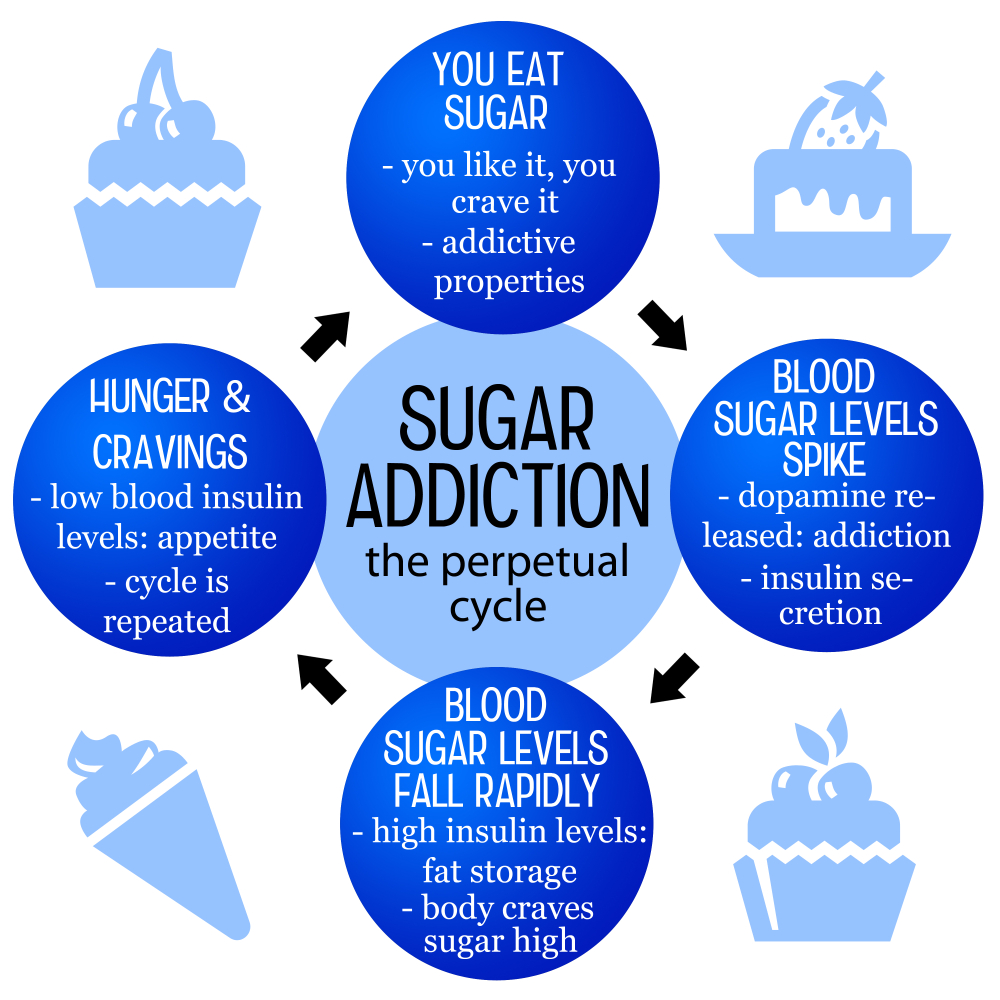
Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked extensive debate among nutritionists and health experts alike. While some research indicates that sugar can lead to cravings and compulsive eating patterns, it does not fit the strict clinical criteria used to classify substances like alcohol or nicotine as addictive. However, the reality is that excessive added sugar consumption, primarily found in processed foods, can significantly impact one’s health and lead to sugar addiction. Understanding the health effects of sugar and the physiological responses to sugar cravings is essential for navigating dietary choices in today’s sugar-laden environment.
The phenomenon often described as sugar addiction revolves around the compulsive desire for sweet substances found abundantly in many processed foods. Many individuals experience significant cravings for sugary products, which can lead to unhealthy eating habits and increased consumption of added sugars. This scenario has become a global health concern, as the excessive intake of sugar has been linked to various health issues, ranging from obesity to metabolic disorders. Exploring the underlying mechanisms of these cravings and their health implications can provide insights into better managing sugar in our diets. Moreover, recognizing the nuances between sugar as a dietary necessity and as a potential source of addiction is crucial for informed nutritional choices.
Understanding Sugar Addiction
The question of whether sugar is addictive has stirred significant debate among nutrition experts. While substances like alcohol and nicotine are classified as addictive based on clinical criteria, sugar does not fit this classification. Nevertheless, research indicates that sugar can trigger cravings and compulsive eating behaviors akin to addiction. This phenomenon is particularly observable in ultra-processed foods loaded with added sugars, which can lead to habitual consumption and withdrawal-like symptoms when intake is reduced.
The addictive qualities attributed to sugar can be largely pinned on its ubiquity in our food system. Ultra-processed foods often contain not only sugars but also unhealthy fats and sodium, creating a highly palatable combination that activates the brain’s pleasure centers. Withdrawal symptoms such as headaches, dizziness, and anxiety can occur when individuals attempt to cut back on sugar-rich diets, though these symptoms vary significantly in severity compared to those associated with true substance addictions.
Health Implications of Sugar Consumption
High sugar intake has been linked to numerous health issues, including obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. The average American consumes nearly 20 teaspoons of added sugar each day, which far exceeds the recommended limit of 6-9 teaspoons as suggested by the American Heart Association. This excessive intake contributes to health complications and can also exacerbate sugar cravings, creating a cycle that’s difficult to break.
Moreover, the health effects of sugar extend beyond physical ailments; they can influence mental well-being as well. Processed foods often lead to a temporary boost in mood followed by a crash that can leave individuals feeling lethargic or anxious. To mitigate these effects, it’s crucial to become more mindful of added sugar consumption and to make informed choices regarding food labels, enabling better management of one’s diet.
The Role of Processed Foods in Sugar Cravings
Processed foods are a major contributor to unhealthy sugar consumption patterns. These foods, engineered for taste and convenience, often contain high amounts of added sugar, which can lead to heightened cravings and a reliance on sugary products. As individuals grow accustomed to high-sugar diets, the pleasure derived from these foods can create a strong preference for sweetness, overshadowing healthier food choices.
Moreover, the immediate gratification provided by sugary snacks can make them difficult to resist. When faced with cravings, many turn to processed foods for their quick energy boost and taste appeal. This reliance reinforces a cycle of consumption—one in which the desire for sugar becomes more pronounced, making it increasingly challenging to reduce intake and switch to healthier alternatives. Education on food choices and gradual reduction in sugar intake can play a pivotal role in breaking this cycle.
Managing Sugar Intake for Better Health
To improve overall health, managing sugar intake is vital. The first step is being aware of how much added sugar is consumed on a daily basis. By reading food labels and becoming familiar with the sugar content of common snacks and drinks, individuals can make informed choices that align better with health recommendations. Reducing sugar does not necessitate a cold turkey approach; gradual reduction can often lead to more sustainable dietary changes.
Incorporating naturally sweet foods—like fruits, which are accompanied by fiber and essential nutrients—can provide satisfaction without the overwhelming health risks associated with excessive added sugars found in processed foods. By embracing a more holistic view of sugar, recognizing its potential benefits and pitfalls, individuals can create a balanced diet that supports long-term health while managing cravings.
The Psychological Effects of Sugar Consumption
Sugar consumption has notable psychological effects that can mirror those of other addictive substances. The enjoyment derived from sweet foods can lead to a temporary mood boost, but this can be followed by lows due to blood sugar crashes. Understanding these patterns is essential for individuals striving to maintain emotional balance and avoid using food as an emotional crutch.
Additionally, individuals might find their mood swings exacerbated by high sugar diets, resulting in increased cravings for sugary foods whenever they experience stress or negative emotions. Building nutritious habits that incorporate a variety of whole foods can help mitigate these emotional triggers, promoting better psychological health alongside physical well-being.
Sugar in Fruits vs. Added Sugars
A crucial distinction exists between naturally occurring sugars found in fruits and added sugars in processed foods. While fruits provide essential vitamins, fiber, and antioxidants, added sugars offer little nutritional value and can contribute to numerous health complications when consumed in excess. Understanding this difference is vital in making healthier dietary choices.
Eating whole fruits can satisfy sugar cravings while also promoting overall health. Unlike added sugars, which can lead to spikes and crashes in energy levels, the natural sugars found in fruit provide a steady source of energy. Including a variety of fruits in one’s diet can support health goals while keeping cravings at bay, all while providing necessary nutrients.
Tips for Reducing Added Sugar Consumption
Reducing added sugar consumption requires both awareness and strategic planning. Start by identifying common sources of added sugar in your diet, such as sugary beverages, snacks, and desserts. Once identified, consider healthier alternatives that fulfill sweet cravings without compromising health.
Another effective strategy is to gradually decrease sugar intake rather than attempt an abrupt elimination. Begin by narrowing consumption of sugary drinks and treating sweets as an occasional indulgence rather than a daily staple. This approach can make the change feel less daunting and is more likely to be sustainable in the long run.
Evaluating Sugar’s Role in a Balanced Diet
In evaluating sugar’s place in a balanced diet, it’s important to recognize that while it can enhance flavor and enjoyment, moderation is key. Understanding portion sizes and the context of sugar consumption can help maintain a balance that avoids the pitfalls associated with excessive intake.
Additionally, context should also consider individual dietary needs and lifestyles. A small amount of sugar can be a part of a healthy, fulfilling diet when consumed responsibly. Focusing on whole foods and making informed choices can empower individuals to enjoy sweetness without sacrificing their overall health and well-being.
The Future of Sugar Research
As health research continues to evolve, understanding the complexities of sugar addiction will become increasingly nuanced. Current studies are focusing on the psychological and physiological effects of sugar consumption and how they may overlap with other addictive behaviors. This ongoing research can provide greater insight into sugar cravings, helping to inform better dietary guidelines.
Future investigations into how processed foods influence sugar addiction may also reveal new avenues for intervention. By identifying triggers associated with sugar cravings in processed food contexts, nutrition experts can develop targeted strategies to help individuals make healthier choices, thereby reducing the prevalence of sugar-related health issues.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like alcohol or nicotine?
While sugar can lead to cravings and compulsive eating, it is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. However, many people experience withdrawal-like symptoms when they reduce or eliminate sugar from their diets due to its presence in ultra-processed foods.
What are the health effects of sugar addiction?
Excessive sugar consumption can lead to health issues such as obesity, diabetes, and heart disease. It’s essential to understand that while sugar may create cravings, having it in moderation is important for health. The average intake is much higher than recommended, thus monitoring sugar levels is crucial.
How do sugar cravings compare to drug addiction?
Sugar cravings can mimic some aspects of drug addiction, as both can involve a desire for immediate gratification. However, the psychological and physical withdrawal symptoms from sugar are generally less severe than those associated with narcotics or alcohol.
What role do processed foods play in sugar addiction?
Processed foods often contain high amounts of added sugars, fats, and sodium, making them highly palatable and easy to overconsume. This can lead to habitual sugar consumption, reinforcing cravings and feeding a cycle of addiction-like behavior without providing nutritional benefits.
Can reducing added sugar consumption lead to withdrawal symptoms?
Yes, when individuals drastically cut back on added sugar, they may experience withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches and anxiety. To minimize these effects, gradually reducing sugar intake rather than quitting cold turkey can lead to better outcomes.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Sugar Addiction Debate | Sugar is not classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine, despite cravings and compulsive behaviors. |
| Physical and Psychological Effects | Withdrawal-like symptoms from sugar reduction may include headaches, anxiety, but are less severe compared to drugs. |
| Ultra-Processed Foods | These foods, high in added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium, can lead to increased cravings and habitual consumption. |
| Recommended Sugar Intake | American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugar to 9 teaspoons for men, 6 for women, and less for children. |
| Balanced Perspective | Moderate sugar intake can enhance flavor and enjoyment, distinguishing it from harmful substances. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? The debate surrounding sugar addiction reveals that while sugar can induce cravings and compulsive eating behaviors, it is not officially classified as an addictive substance like alcohol or nicotine. The relationship with sugar is complex, as it plays a vital role in our diet and can enhance our enjoyment of food. However, it’s crucial to manage sugar intake wisely to prevent excessive consumption, especially from ultra-processed foods. Maintaining a balance and understanding the recommended intake can lead to healthier dietary habits.