Suicide prevention for older adults is a critical topic that demands immediate attention, especially given that individuals aged 75 and older represent the highest risk group for suicide among all ages. Despite alarming elderly suicide rates, resources tailored specifically for this demographic are shockingly scarce. A recent study conducted by researchers at Harvard-affiliated McLean Hospital underscores the pressing need for improved mental health resources aimed at seniors. As physical health issues compound with loneliness and social isolation, older adults increasingly seek online suicide prevention support that is not readily available. Thus, advocating for greater awareness and accessibility in mental health for seniors is paramount to helping this vulnerable population.
Addressing the issue of suicide among the elderly population is vital as it highlights the urgent need for specialized intervention strategies. Many senior citizens, facing high suicide rates, find themselves in a vulnerable position due to various factors, including social isolation and lack of accessible mental health services. This calls for a fresh approach to geriatric psychiatry that prioritizes mental wellness and integrates online suicide prevention resources tailored for older adults. Emphasizing the importance of mental health for seniors, we must advocate for effective outreach and support systems that cater specifically to their unique challenges. By bridging the gap between this demographic and essential mental health resources, we can foster a safer and more supportive environment for older individuals.
Understanding Elderly Suicide Rates
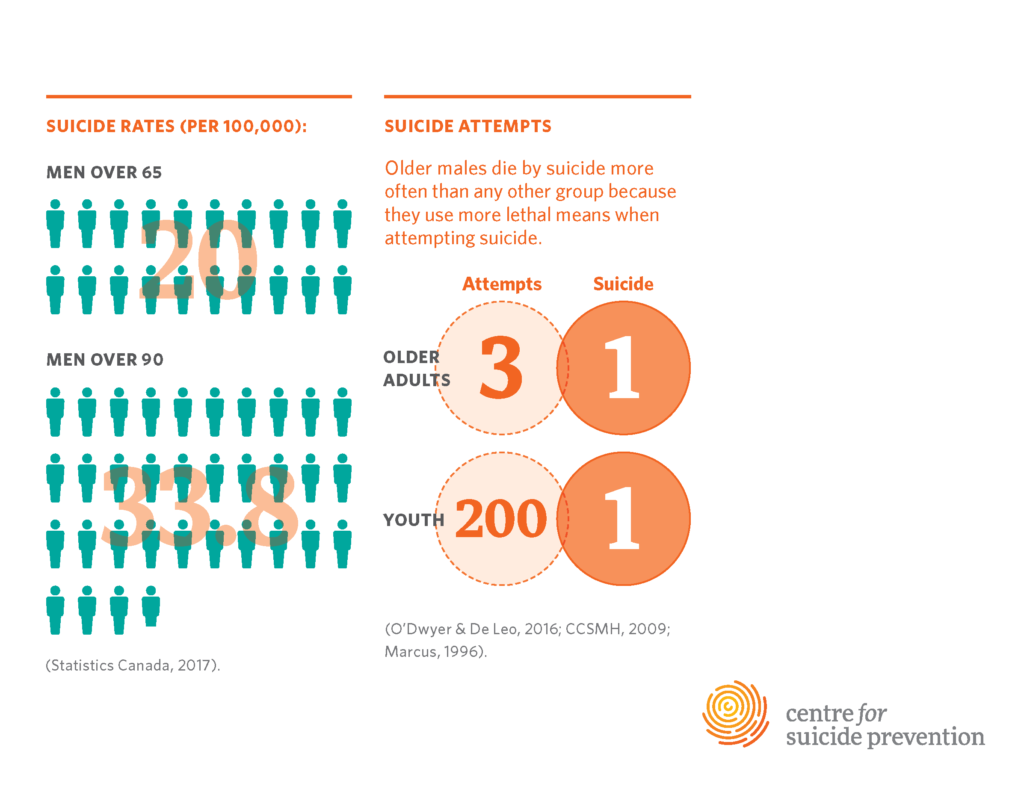
Elderly suicide rates are alarmingly high, with adults aged 75 and older experiencing the highest incidence of suicide among all age groups. Recent data from the CDC reveals that this demographic has a suicide rate of 20.3 per 100,000, highlighting a critical public health issue that demands immediate attention. Factors contributing to these increased rates include social isolation, mental health challenges, and a lack of adequate support services tailored to the elderly population. As we delve deeper into understanding these statistics, it becomes clear that many older adults face unique stressors that can lead to severe mental health crises.
Moreover, the increased likelihood of loneliness and diminished social connections can exacerbate mental health issues among seniors. With the shifting landscape of healthcare and mental health resources, it is essential to examine how these factors intertwine to influence elderly suicide rates. By fostering awareness around these statistics and their underlying causes, we can better advocate for resources that address the needs of our older population, particularly in light of the existing imbalance in mental health services available for them.
The Role of Mental Health Resources in Suicide Prevention
Mental health resources play a crucial role in addressing the rising rates of suicide among older adults. Comprehensive mental health support tailored specifically for seniors is fundamental in combatting the trends highlighted in recent studies. Access to geriatric psychiatry services can ensure that elder patients receive the specialized care they require. However, despite the acknowledged need for more tailored resources, many seniors find these services difficult to access. There is an urgent requirement for enhanced visibility of mental health resources that cater explicitly to the elderly, ensuring that they can find the help they need when they need it.
Additionally, integrating mental health resources through community programs and online platforms can significantly improve outcomes for older adults at risk of suicide. By capitalizing on the increasing comfort level seniors have with technology, initiatives that promote online suicide prevention resources can be expanded. These resources must not only educate but also empower older adults to seek support proactively. Thus, the strategic development of mental health resources is indispensable in our collective effort to reduce suicide rates within the older population.
Promoting Online Suicide Prevention Strategies
Online suicide prevention strategies have emerged as a viable option for reaching older adults in crisis. With an increasing number of seniors adopting technology to seek health information, creating user-friendly and accessible online platforms can bridge the gap in resources specifically aimed at this demographic. Tailored online campaigns can provide crucial information, support networks, and emergency contacts for older adults who may be experiencing suicidal thoughts or feelings of isolation. Implementing these strategies effectively requires an understanding of the unique challenges faced by seniors, ensuring that the content is relatable and easily navigable.
Moreover, developing educational content around online suicide prevention can help destigmatize mental health discussions among older adults. By fostering an environment where seeking help is normalized, we can encourage seniors to utilize these online resources without fear or shame. The importance of integrating technology in suicide prevention cannot be overstated; these strategies not only increase accessibility but also enable a confidential means for older adults to engage with mental health services and peer support.
The Importance of Tailored Prevention Programming
Addressing the specific needs of older adults requires the development of tailored prevention programming that is mindful of their unique healthcare challenges. Unlike younger populations, older adults may face more complex health issues that impact their mental health, and suicide prevention initiatives must recognize this difference. Programs designed to focus on fostering social connections, mental wellness, and active engagement in the community can enhance the lives of older adults and mitigate their risk of suicidal ideation. By prioritizing programs that reflect an understanding of geriatric needs, we can not only raise awareness but also contribute to a more supportive environment for seniors.
Furthermore, collaboration between mental health professionals, community organizations, and public health officials is vital in crafting effective prevention programs that resonate with older adults. Investing in these tailored initiatives can lead to better mental health outcomes and more robust support systems that older individuals can rely on. It is crucial for policymakers and organizations to understand that improving mental health for seniors is a multifaceted approach that requires joint efforts and ongoing commitment.
Addressing Systemic Biases Against Older Adults
Systemic biases against older adults can lead to a significant underrepresentation in both research and the development of mental health resources. These biases may contribute to the neglect of the mental healthcare needs of seniors, with many services focusing primarily on younger populations. Recognizing and addressing these biases is fundamental in realigning mental health resources towards those most vulnerable—our older community members. This means not only acknowledging the unique challenges they face but also ensuring their voices are included in discussions and strategies regarding mental health support.
Furthermore, addressing these systemic issues requires a concerted push for inclusivity in mental health research and policy-making. Older adults need to be actively represented in studies that inform mental health practices, allowing their specific conditions and needs to be understood and met. By challenging existing biases and advocating for a more equitable approach in delivering mental health resources, we can make strides towards reducing the stigma around aging, mental health, and suicide prevention—ultimately leading to a healthier, more supported older population.
Increasing Funding for Elderly Mental Health Initiatives
The relationship between increased funding and improved mental health resources for older adults cannot be overlooked. Adequate financial support is critical to developing and sustaining programs that specifically target the needs of seniors at risk of suicide. Current funding streams often lack the focus needed to address the complexities involved in geriatric mental health. Consequently, a concerted effort must be made to petition for increased funding from both public and private sectors to enhance the suicide prevention landscape for the elderly.
Investing in mental health initiatives that cater to seniors can lead to significant advancements in suicide prevention efforts. This includes funding for research aimed at improving geriatric psychiatry practices, as well as community outreach programs that encourage social connectedness and mental wellness among older adults. By championing increased financial resources and supporting programs dedicated to mental health for seniors, we can pave the way for more effective suicide prevention strategies tailored to this vulnerable population.
Building Community Support Systems for Seniors
Community support systems play a pivotal role in ensuring that older adults have access to the resources they need for mental health and suicide prevention. Establishing local networks that incorporate volunteer services, peer support groups, and professional counseling can create a safety net for seniors who may be experiencing feelings of isolation or depression. By fostering strong community bonds, we can help older adults feel more connected and less alone, which is crucial in mitigating the risk of suicide.
Furthermore, encouraging community inclusivity and engagement can empower older adults to seek help and support from their peers. Programs that bring together seniors for social activities, discussions about mental health, and group therapy can enhance their sense of belonging. By building robust community support systems and creating environments where older adults feel safe to express their mental health struggles, we can make significant strides in suicide prevention, ultimately leading to healthier and more fulfilled lives for our seniors.
The Need for Awareness and Education on Elderly Mental Health
Raising awareness and educating the public about elderly mental health issues is essential in combating the rising rates of suicide among seniors. Community education initiatives can provide insight into the unique challenges faced by older adults, fostering empathy and understanding. Through seminars, workshops, and local outreach programs, we can help dispel misconceptions surrounding mental health and aging, equipping families and caregivers with the knowledge to recognize the signs of mental distress in seniors.
Moreover, integrating education about suicide prevention into broader health promotion campaigns can significantly impact public perception and responsiveness to older adults in crisis. By enhancing understanding and reducing stigma, we can encourage individuals to support elders in need of mental health resources. Creating a culture of awareness helps ensure that older adults are seen and heard, paving the way for a more supportive environment that prioritizes their mental health needs.
Innovative Solutions for Enhancing Access to Mental Health Care
Innovation in mental health care access is critical for ensuring that older adults receive the support they need. Implementing telehealth services, for example, can address barriers that many seniors face, such as mobility issues or transportation difficulties. With technology allowing for remote consultations, older adults can connect with geriatric mental health professionals from the comfort of their homes. This kind of service can significantly broaden the reach of mental health resources, making them more accessible to those who may otherwise remain isolated.
Additionally, the adaptation of existing mental health resources to better suit the elderly demographic can enhance usability and effectiveness. By simplifying processes, ensuring user-friendly interfaces, and providing clear instructions, online mental health platforms can be more inclusive for older adults. Continuous innovation in mental health delivery is necessary to meet the evolving needs of seniors and to ensure that they are not left behind in the fight against suicide.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the suicide prevention strategies specifically designed for older adults?
Suicide prevention strategies for older adults focus on addressing their specific mental health needs. These include increasing access to mental health resources, providing targeted community outreach programs, and promoting social engagement activities to combat isolation. Tailored training for healthcare providers in geriatric psychiatry also plays a vital role in identifying and supporting at-risk seniors.
How do elderly suicide rates compare to other age groups?
Elderly suicide rates are significantly higher than those in younger populations, with adults aged 75 and older experiencing a rate of 20.3 per 100,000, according to the CDC. This stark statistic highlights the urgent need for specialized suicide prevention efforts aimed at older adults, particularly as rates in younger age groups have seen declines.
Where can older adults find mental health resources for suicide prevention?
Older adults can find mental health resources for suicide prevention through websites of recognized national organizations, local mental health service providers, and community centers. It is essential that these resources are designed to be age-friendly and easily accessible online, addressing the unique challenges faced by the elderly.
What role does geriatric psychiatry play in suicide prevention for older adults?
Geriatric psychiatry plays a crucial role in suicide prevention by providing specialized training and insight into the mental health issues affecting older adults. This field focuses on the unique psychological and physiological needs of seniors, enabling clinicians to offer more effective interventions and support tailored specifically to this age group.
How can online suicide prevention efforts be improved for older adults?
Online suicide prevention efforts can be improved for older adults by making resources more accessible and visible. This includes creating age-appropriate websites, enhancing outreach campaigns that target older individuals, and developing online support groups that consider the technological proficiency of seniors. Focusing on these areas can help bridge the gap in current suicide prevention efforts.
What factors contribute to the high rates of suicide among older adults?
Several factors contribute to high suicide rates among older adults, including social isolation, loss of loved ones, chronic health conditions, and lack of accessible mental health resources. Additionally, stigmas surrounding mental health can prevent seniors from seeking help, highlighting the need for effective outreach and tailored support services.
Are there any specific online suicide prevention programs for seniors?
While there are some online suicide prevention programs targeting seniors, they are often limited. Effective programs should be specifically designed to address the needs of older adults, offering resources like virtual counseling, interaction with peers, and accessible information about mental health assistance tailored to their experiences.
What preventive measures can families take to support older adults at risk of suicide?
Families can support older adults at risk of suicide by maintaining open lines of communication, encouraging social interactions, facilitating access to mental health resources, and fostering an understanding of the signs of depression or suicidal thoughts. Regular check-ins and engaging activities can significantly diminish feelings of loneliness and isolation.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Older Adults’ Suicide Rates | Older adults aged 75 and older have the highest suicide rates of any age group, with 20.3 per 100,000 according to the CDC. |
| Lack of Resources | National suicide prevention organizations do not provide sufficient resources specifically targeting older adults, despite acknowledging their high risk. |
| Research Findings | A study led by McLean Hospital researchers emphasizes a significant imbalance in online suicide prevention efforts for older adults. |
| Need for Campaigns | There is an urgent need for public-facing suicide prevention campaigns tailored to older adults due to rising suicide rates and increased social isolation. |
| Future Steps | Targeted campaigns, increased funding, and tailored programming are essential to address the unique healthcare needs of older adults in suicide prevention efforts. |
Summary
Suicide prevention for older adults is a critical but often overlooked issue, as this demographic holds the highest risk for suicide among all age groups. Recent research indicates a stark lack of accessible resources specifically addressing their needs. With rising rates of suicide in those aged 75 and older, accompanied by factors such as social isolation and loneliness, it is essential to elevate awareness and implementation of tailored suicide prevention strategies. Engaging older adults with effective campaigns and improving their access to needed resources can significantly mitigate the impact of this concerning trend.